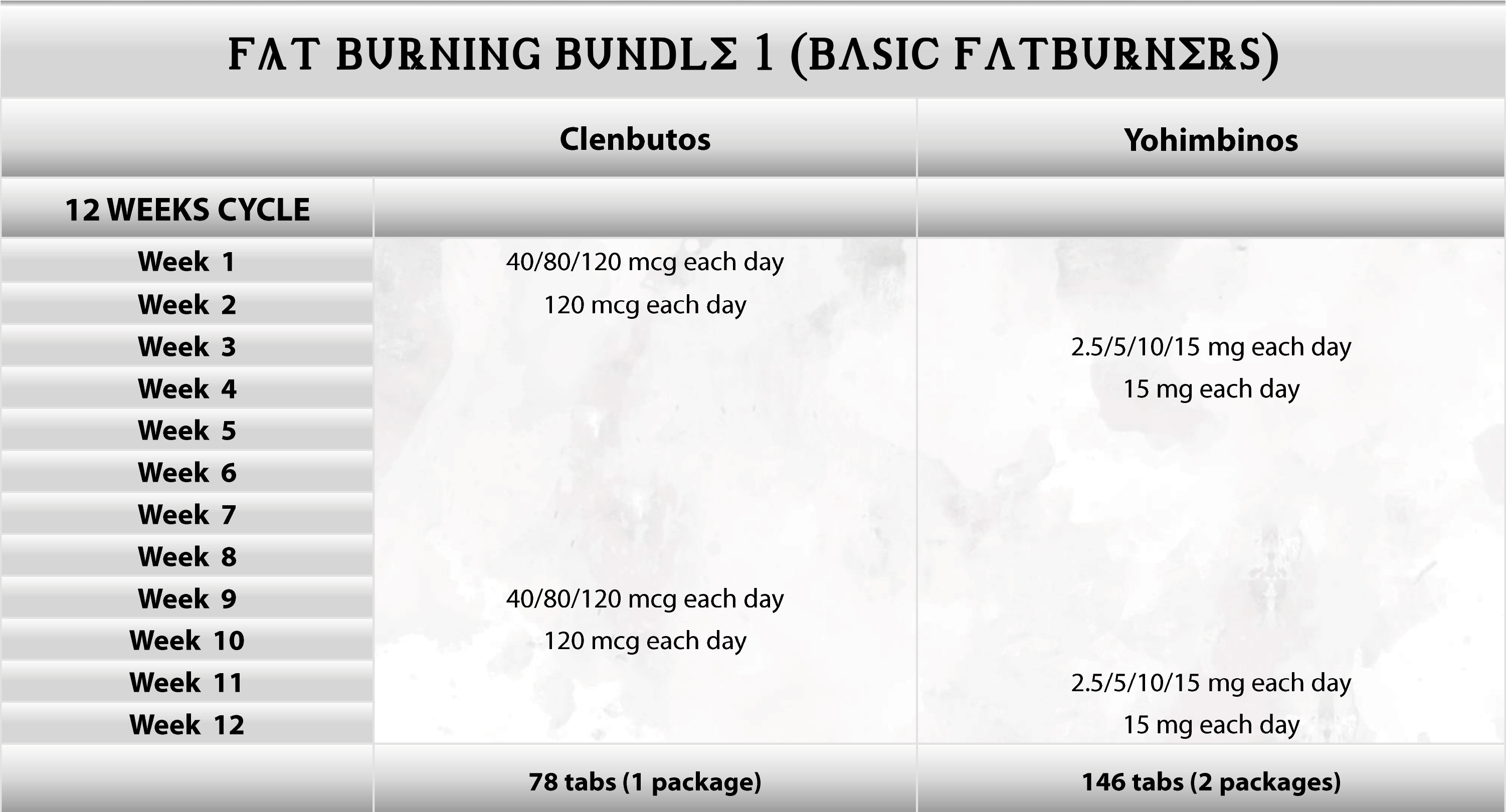
Fat Loss Cycle: A 12-Week Approach
This cycle features a combination of fat-burning drugs designed to effectively reduce body fat. These medications can be used individually or in conjunction for a more potent effect.
12-Week Duration Rationale
This bundle is tailored for a 12-week duration. While you can adjust it to suit your individual preferences, we recommend this period for optimal results. A 12-week timeframe provides sufficient time for significant body transformation while adhering to a diet and utilizing fat-burning drugs.
Cycling Methodology
This cycle incorporates cyclical use of drugs such as yohimbine and clenbuterol. Simultaneous use is discouraged due to the risk of synergistic side effects like tachycardia, caused by excessive nervous system stimulation. Additionally, prolonged individual use of each drug can lead to diminished effectiveness. Therefore, after a clenbuterol phase, a pause is recommended, during which yohimbine can be incorporated.
Anabolic Steroid Integration
While these drugs can yield substantial results on their own, they often achieve greater effectiveness when combined with an anabolic steroid cycle. Given that many steroid cycles also span 12 weeks, this timeframe aligns perfectly for simultaneous fat-burning efforts.
We recommend utilizing anabolic steroids that promote pure muscle mass development, such as trenbolone, stanozolol, oxandrolone, drostanolone, dihydroboldenone, methenolone, and others. Avoid classic bulking steroids like nandrolone and excessive testosterone dosages, as these can lead to fluid retention and a puffy appearance during the cycle, potentially hindering visual progress. It's also crucial to monitor estradiol and prolactin levels when using these drugs, as elevated levels can also hinder fat loss.
Clenbuterol: A Deeper Dive
Clenbuterol is a sympathomimetic agent initially developed for respiratory conditions like bronchial asthma. However, its ability to boost metabolic activity and reduce fat mass has gained popularity among athletes and bodybuilders. Often utilized as a fat burner, clenbuterol promotes increased thermogenesis, leading to greater heat production and energy expenditure, ultimately contributing to fat reduction and improved muscle definition. Clenbuterol's fat-burning effects stem from several mechanisms:
Cellular Beta-Adrenergic Stimulation
Clenbuterol activates beta-adrenergic receptors in the body, which are linked to metabolic processes including increased oxygen and energy consumption. This leads to enhanced metabolism and calorie utilization for energy production. Here's a more detailed breakdown of its adrenoreceptor effects:
Clenbuterol acts as an agonist for beta-adrenergic receptors, which are proteins on cell surfaces that respond to adrenaline and similar molecules. While humans have various subtypes of beta-adrenergic receptors, the primary ones affected by clenbuterol are beta-2-adrenergic receptors. When clenbuterol binds to these receptors, it triggers an intracellular signaling pathway that elevates cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) levels within the cell. cAMP plays a crucial role in regulating cell metabolism and energy consumption. Increased cAMP levels activate the protein kinase cascade, ultimately boosting energy consumption, leading to heightened metabolism and calorie utilization for energy production.
Lipase Activation
Clenbuterol activates beta-2-adrenergic receptors found on the surface of fat cells. This action initiates an intracellular signaling pathway that activates lipase, an enzyme responsible for breaking down triglycerides (the primary fatty molecules) in fat cells into glycerin and fatty acids. This process is known as lipolysis.
After lipolysis, fatty acids are released from fat cells into the bloodstream. They are then transported to cell mitochondria, where they undergo beta oxidation, generating acetyl-CoA, which ultimately contributes to the production of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the primary energy molecule in the cell. Mobilizing fat reserves allows the body to utilize fats as an energy source, resulting in reduced fat mass. Clenbuterol's stimulation of this process contributes to its popularity among those seeking fat loss.
Thermogenesis Enhancement
Clenbuterol contributes to increased thermogenesis, meaning a rise in heat production by the body. This is driven by increased mitochondrial activity, which is involved in energy production. Elevated thermogenesis leads to additional calorie expenditure.
Clenbuterol enhances mitochondrial activity, these "energy powerhouses" of the cell. Mitochondria are essential in the production of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the primary energy molecule in the cell. Increased mitochondrial activity boosts metabolism and calorie consumption in the body. This translates to greater energy expenditure for bodily functions.
The increased heat production within the body, stemming from enhanced mitochondrial activity and metabolism, leads to increased thermogenesis. Thermogenesis, the process of the body generating heat, requires additional energy, which is drawn from fat reserves. As a result of increased thermogenesis and calorie consumption, the body begins utilizing fats as an energy source, leading to decreased fat mass as fats are broken down and utilized for energy production.
Appetite Suppression
Clenbuterol can influence appetite centers in the brain, potentially reducing food cravings. This can contribute to a decrease in overall calorie intake. While clenbuterol may affect appetite suppression, this mechanism isn't as well understood as many of its other actions.
It's important to note that appetite suppression under clenbuterol's influence can be individual and may not occur in all users. Additionally, appetite suppression may be temporary, and upon discontinuing clenbuterol, appetite may return to normal levels.
● Clenbuterol impacts appetite centers in the brain, such as the hypothalamus, which regulate feelings of hunger and satiety.
● Elevated cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP): As previously mentioned, clenbuterol stimulates an increase in cAMP levels within cells. cAMP is a significant molecule in the signaling pathway associated with appetite and metabolism.
● Neurotransmitter Regulation: Clenbuterol can influence neurotransmitters like serotonin and norepinephrine, which play a role in regulating appetite. It may affect these neurotransmitters, helping to reduce hunger.
● Hormone Modulation: Clenbuterol can also affect the body's hormonal balance, which can influence appetite. For instance, it can increase adrenaline levels, potentially contributing to appetite suppression.
Tolerance Development
Clenbuterol, like many other drugs and pharmacological agents, can lead to tolerance in the body. This means that higher doses may be required over time to achieve the same effect. This process involves several mechanisms:
● Receptor Desensitization: Prolonged clenbuterol exposure to beta-adrenergic receptors can lead to desensitization, a decrease in receptor sensitivity to the drug. This necessitates a higher clenbuterol dosage to achieve the same effect.
● Reduced Duration of Action: Initially, clenbuterol may exert a more pronounced effect on thermogenesis and fat burning, but over time, its duration of action may decrease, resulting in a less noticeable effect.
To prevent or slow down the development of clenbuterol tolerance, cyclic use can be employed. Clenbuterol can be used in cycles with breaks in between. For example, two weeks of use followed by a four-week break, during which we recommend using alternative fat burners like yohimbine, to ensure continued progress. This approach can help maintain receptor sensitivity.
It's essential to recognize that clenbuterol's effectiveness as a fat burner can vary individually and depends on numerous factors, including dosage, duration of use, and overall human health.
For a comprehensive overview of this product's effects, follow this link
Yohimbine: A Detailed Examination
Yohimbine is an alkaloid derived from the bark of the yohimbe tree (Pausinystalia yohimbe) and certain other plants. It is utilized as a fat-burning supplement and can influence fat metabolism. Here's a thorough explanation of yohimbine's mechanism of action on fat burning:
Alpha-2-Adrenergic Receptor Antagonism
Yohimbine functions as an antagonist of alpha-2-adrenergic receptors, located on the surface of fat cells. When activated, these receptors inhibit lipolysis (fat breakdown). By antagonizing alpha-2-adrenergic receptors, yohimbine removes this inhibitory effect, allowing fats to be broken down more readily. Blocking these receptors enhances lipase activity, the enzyme that breaks down fats into glycerin and fatty acids. This process releases fatty acids from fat cells into the bloodstream. These fatty acids can be used as an energy source during physical activity, promoting fat burning.
Increased Adrenaline Levels
Yohimbine also contributes to increased adrenaline levels in the body. Adrenaline, a hormone and neurotransmitter, boosts metabolism and mobilizes fat reserves. This leads to heightened energy consumption and an accelerated fat-burning process. Adrenaline activates beta-adrenergic receptors on the surface of fat cells, stimulating lipolysis. This results in the release of fatty acids from fat cells into the bloodstream for use as an energy source.
Central Nervous System Stimulation
Yohimbine can exert a stimulating effect on the central nervous system, potentially enhancing energy levels and physical activity. This can contribute to more vigorous workouts and increased overall calorie expenditure.
Appetite Suppression
Some users report that yohimbine can reduce appetite. Yohimbine may influence appetite by affecting appetite centers in the brain. This can potentially decrease food cravings and consequently, calorie intake.
Tolerance Development
Tolerance to yohimbine can develop in some individuals, requiring increased dosages over time to achieve the same effect. This process is linked to several mechanisms:
● Receptor Desensitization: Prolonged exposure of yohimbine to alpha-2-adrenergic receptors located on the surface of fat cells can lead to desensitization of these receptors. This means they become less sensitive to yohimbine's effects, requiring a higher dosage for desired outcomes.
● Reduced Effectiveness: Initially, yohimbine may exhibit a more pronounced effect on fat burning and metabolism. However, over time, this effect may diminish, reducing yohimbine's effectiveness.
To prevent or slow down the development of yohimbine tolerance, the following strategies can be implemented:
● Cyclic Use: Many individuals employ yohimbine in cycles with breaks in between. For example, two weeks of use followed by a four-week break. This can help maintain receptor sensitivity.
● Avoidance of Long-Term Use: Yohimbine is best utilized in short-term cycles, adhering to recommended dosages.
Important Cautions
It is crucial to exercise caution when using yohimbine and follow the guidance of a healthcare professional. Yohimbine can cause side effects and has specific medical contraindications. It's important to acknowledge that yohimbine's efficacy and safety are individual, and it is not suitable for everyone. Before initiating yohimbine or any other fat-burning supplements, consulting with a qualified healthcare professional is essential to consider individual characteristics and risks. The effectiveness of yohimbine can vary between individuals.
For a comprehensive overview of this product's effects, follow this link
